How to calculate the retail price taking into account the supplier's discount and RRP control
RRP - the supplier's recommended retail price for its products. It is advisory in nature. However, many wholesalers, when signing a cooperation agreement, set a minimum and maximum threshold for the seller's markup on their goods, with the intention of stopping their shipment in case of violation of the terms of the contract.
Controlling the recommended retail price (RRP) will avoid such sanctions and set a normal margin, allowing you to make a profit and maintain stable demand. A program for automating an online store from a developer company can not only automate the control of the RRP, but also automate the operation of the store completely.
Reasons that affect the value of the margin on the goods
To establish the optimal retail price, it is necessary to correctly calculate the trade margin. It is influenced by a number of factors:
- The product and its characteristics. The amount of the premium cannot be fixed. It depends on the quality, the relevance of the offer to the end consumer, the fame and competitiveness of its manufacturer. High quality products that are in stable demand allow you to set a higher margin than highly specialized ones, the same goes for products of well-known brands. New items that are at the peak of popularity in a certain period of time also allow you to increase margins.
- Trading expenses. In addition to the purchase price of the product, the markup includes all costs associated with the sale of the product, including logistics, shipping, manager salaries, warehousing, advertising and promotion.
- Taxes. If fiscal payments are not included in the retail price, there is a risk of incurring an after-tax loss instead of making a profit.
How to Avoid Mistakes When Calculating Markups on Goods
To calculate the price of a product, taking into account the supplier's discount, it is necessary to take into account the financial capabilities of the end buyer. There is no clearly defined strategy or ratios. Most often, average indicators for certain market segments are used for calculations:
- For accessories, souvenirs, jewelry and bijouterie - 100+%, as they have the lowest cost and are in stable demand.
- For clothing and footwear, the markup varies depending on seasonality, type, quality, properties and can be 45-105%, in addition, seasonal discounts and sales are common in this product segment.
- Cosmetics can be sold with a markup of up to 75%, depending on the type and popularity of a particular product and its manufacturer.
- For automotive products (spare parts for cars and motorcycles, accessories, consumables) - the end result may differ from the purchase by only 30-35%.
- Home and office supplies can cost 25-75% more.
In monetary terms, the maximum allowable margin can be found by multiplying the purchase price by the average for the selected segment.
When calculating, you can also focus on the prices of competitors, since often different online stores make purchases in the same place.
How to automate the control of RRP and prices in an online store
You can automate the control of RRP and prices with the Elbuz program from Elbuz.
Advantages of price control and monitoring with Elbuz
With the help of Elbuz Elbuz software, you can solve a number of online business tasks:
- Monitor the prices of suppliers and competitors automatically from the sites specified by the user (as soon as there are changes in the prices, the program will send a notification or make corrections in your store itself to avoid sales at a loss).
- Download products from any online source to compare pricing and availability.
- Combine and structure data from different sources with the possibility of a common search.
- Make the pricing strategy flexible using advanced formulas and a user-generated algorithm, update and monitor the relevance of the price list daily.
- Make profitable and competitive offers to customers based on data from parsing and analysis of competitor sites in order to increase sales.
- Upload up-to-date information from the software to any convenient XLS, XML, CSV format or directly to the site
In Elbuz, you have access to various types and methods of markup for products downloaded from price lists, taking into account discounts from suppliers, as well as taking into account competitors' prices.
The order of work is as follows: we price the products from the price lists of suppliers based on their wholesale price, get our retail price with our interest, if necessary, compare the price that we received with a competitive price and do not forget about RRP control, then update the base catalog with new prices and upload these data to the site.
Types of markup applied to products from the price list. As you can see, there are a lot of them, so this gives you the opportunity to get exactly what you could not do before. 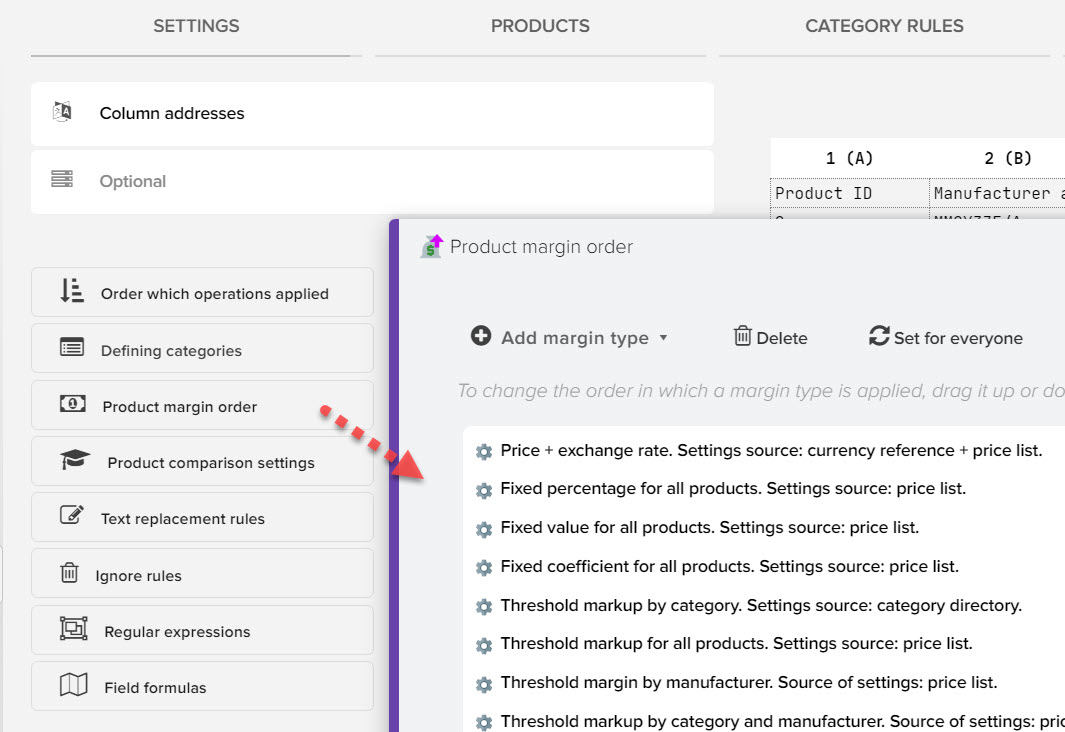
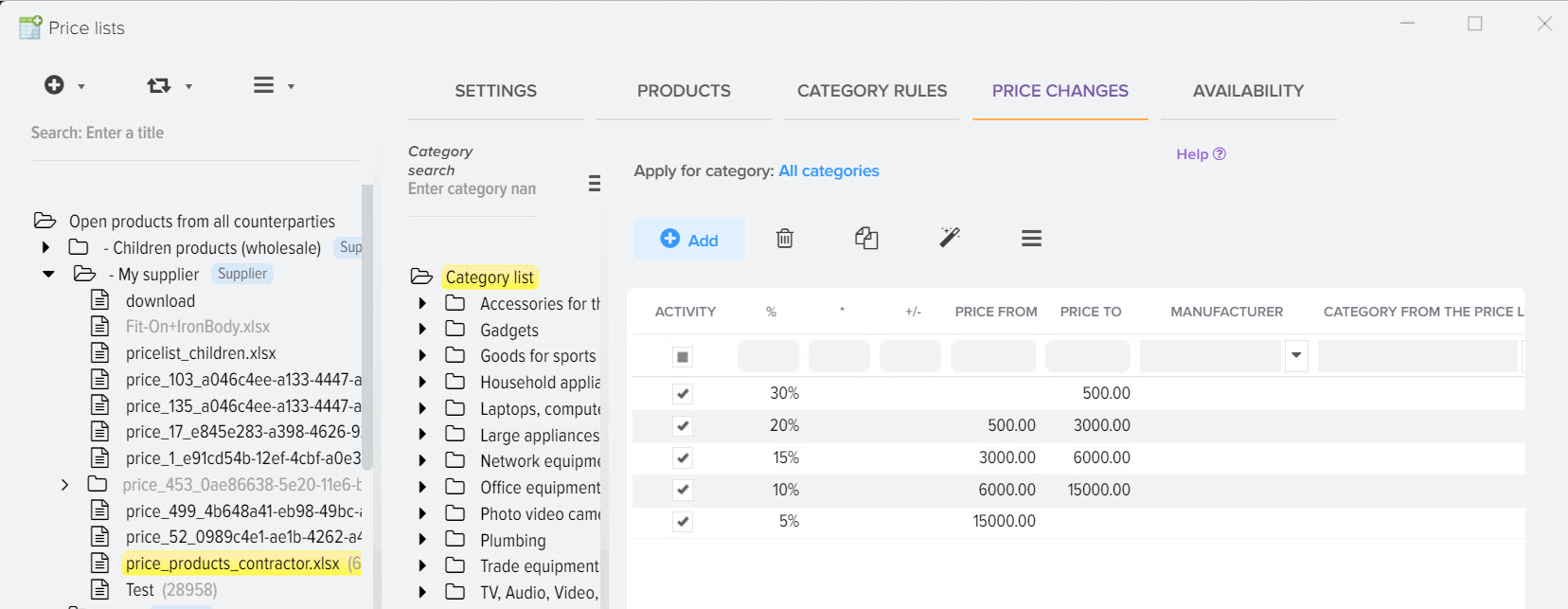
By default, all types of markups that can be applied to products from the price list are active. You just have to set up the rules for their application, that is, prescribe the markups / discounts you need. The main part of markups is set in the "Markup / Discount" tab for the selected price list. 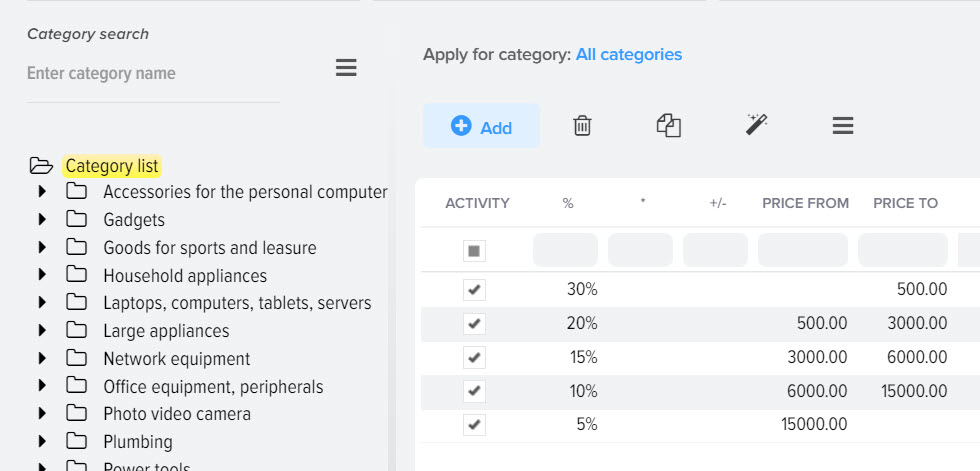
You can set a markup rule for a specific category of products in the base catalog, or for all at once. To set a markup without taking into account categories, select the "List of categories" item on the left and click the "+" button to add a markup rule.
You can set a fixed markup without taking into account the price of the products from the price list or taking into account the price - a threshold markup.
If the line with the markup rule does not contain values in the "Price from" and "Price to" fields, then the markup is applied to products without taking into account the price.
You can set the markup using different types of price calculation:
- Percentage (column %).
A percentage is added to the price. For example, a markup of 10%, a product costs 100EUR, the cost of a product with a markup is 110EUR. - Coefficient (column *).
The price of the product is multiplied by the value specified in this field. For example, the markup coefficient is 1. 2, the product costs 100EUR, the cost of the product with a markup is 120EUR. - Value (column +).
The specified value is added to the price of the item. For example, the value is 15, the product costs 100EUR, the cost of the product with a markup is 115EUR.
All of the listed types can be combined, that is, you can use several types of markups at once, for example, Percentage + Coefficient + Value, in which case the markup on the product is summed up. To use multiple types of markups (or discounts), specify them on separate lines (add multiple lines to the grid).
If a negative value is specified, then a discount is applied to the product price (the specified values are subtracted).
Description of markup rules grid fields
- Activity
Markup rule setting active flag. For example, you can temporarily disable a rule without deleting its settings. - Price from
The price from the price list is set from which the threshold markup can be applied. - Price up to
The price from the price list is set up to which the threshold markup can be applied.
Goal: Create a price range rule and apply the specified markup value to this range. - Manufacturer
You can specify for which manufacturer the markup should be applied, while the manufacturer must be defined for the product. - Price category
You can specify which category from the price list to apply the markup to. The list of available categories from the price list will be available after setting up the definition of categories in the price list. - Source field
By default, the value source for the markup is the Price field. You can load several prices from the price list into different fields, while specifying in this setting which field should be used for the markup rule. - Destination field
By default, the markup storage destination is the Price field. You can change this by specifying in which field the markup is saved.
Setting the source and destination fields is purely individual and you rarely need to change them, so if you are a beginner, you should not change them. - Application procedure
You can set the order in which markup rules are applied. For example, first apply a -10% discount to all products, and then apply a threshold markup. - Note
Provide text that will help you further understand what this markup rule does, who asked for it, why, etc.
Additional filter
For each markup rule, you can set an individual filter based on the values of products from the price list. For example, you can apply a markup only for products that have a 2-year warranty. 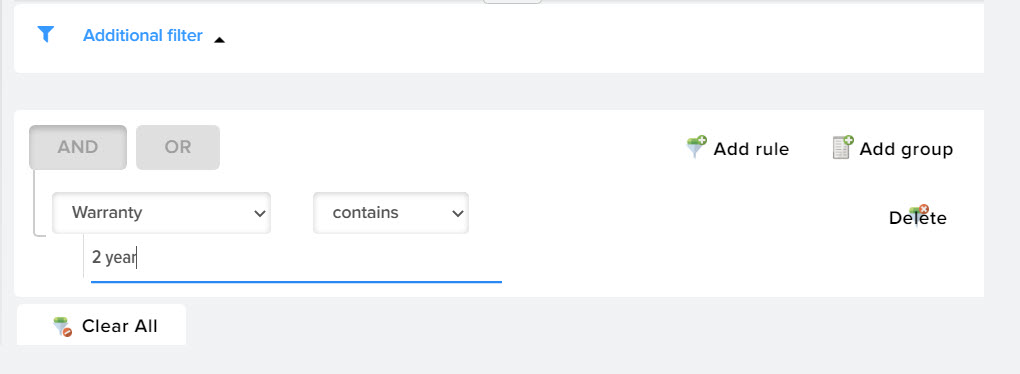
Threshold markup on goods
The markup is configured for the base currency of the database, that is, the price thresholds must be set in the base currency.
An example of pricing when using a threshold markup. For example, the following thresholds are created:
- from 0 to 100 30%
- from 100. 01 to 500 20%
- from 500. 01 to 1000 15%
- from 1001. 01 to 0 10%
Calculation example:
- Product No. 1, price 55 rubles, falls into the first rule of the threshold from 0 to 100, calculation: 55 rubles. + 30% = 71. 5 rubles. (with a multiplicity value of 5, the output price will be 75 rubles).
- Product No. 2, price 1350 rubles, falls into the fourth rule of the threshold from 1000. 01 to 0. If the "Price to" column is set to zero, then products with a price of 1001 rubles or more fall into this rule. and up to ∞, that is, all products whose price is higher than 1001 rubles, calculation: 1350 rubles. + 10% = 1485 rub.
Apply markup to child categories
If you set up a markup for product categories of the base catalog, then the function of copying the markup rules for child categories (which are included in the category you have chosen, are its descendants) will be useful to you.
To do this, you need to set the markup for the main category, then click the "Apply markup for child categories" button.
In this example, we set up a markup of 10% for the "Water Heaters" category, after copying the markup, all "Boilers. . . " categories will receive a markup of 10%. This feature will speed up the process of setting markup rules by category for each price list. 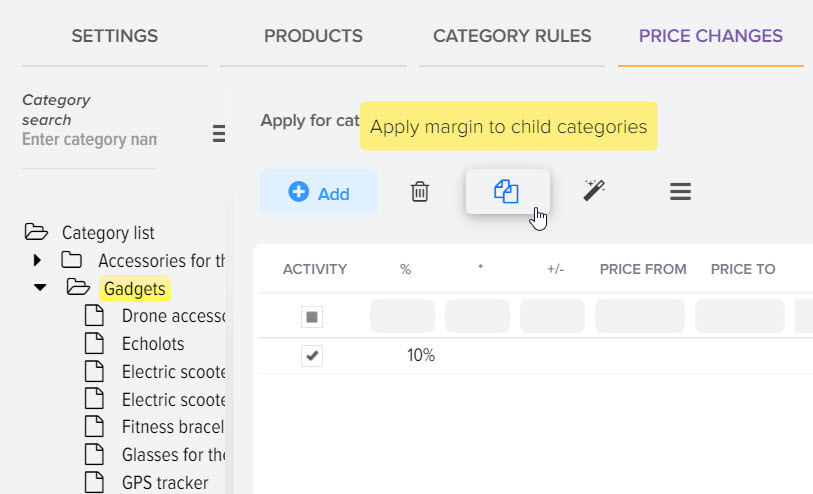
General markup rules by category for all price lists.
If your markup rules for categories of the base catalog are the same for all price lists, then you should set it up in the category directory, this will significantly reduce your time for setting up, because you will not need to register the same settings for each price list. 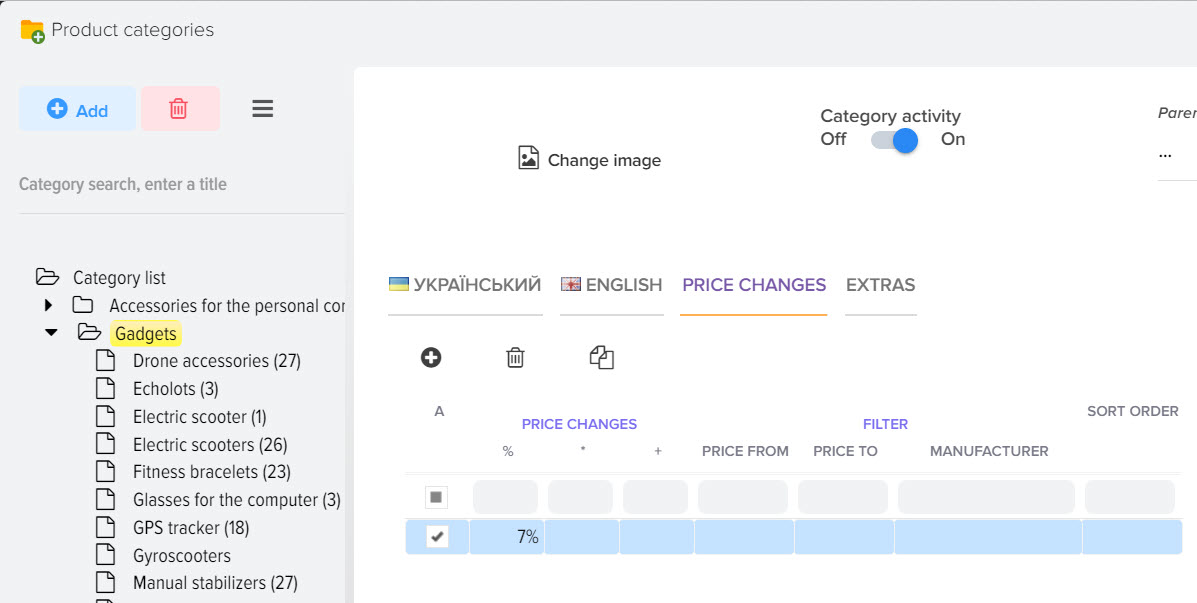
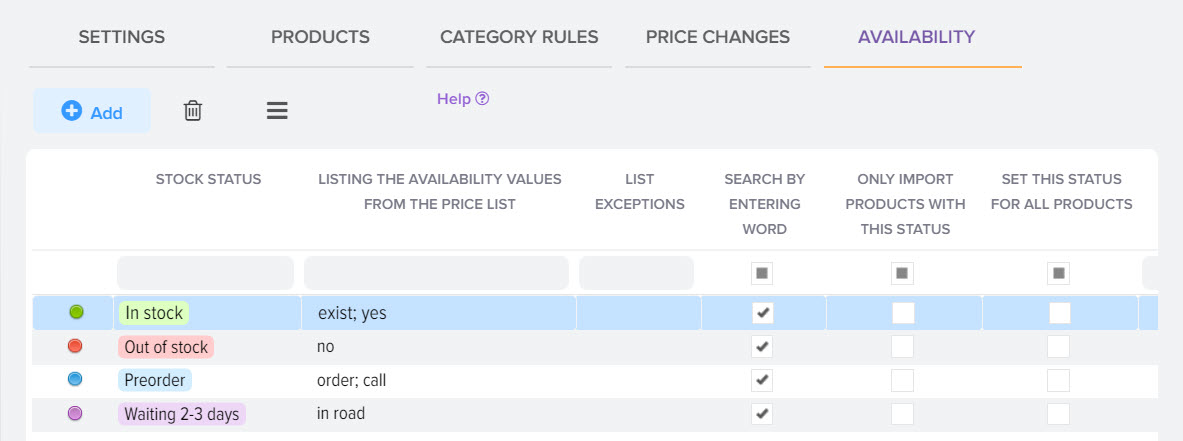
Availability based markup
Sometimes you need to set up a markup based on the status of the availability of goods, you can easily do this by setting the required markup value for the status you need 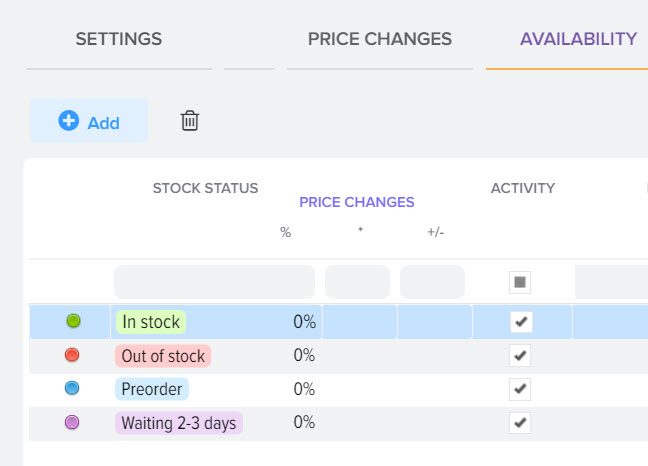
Restricting the application of markup types
You can limit the use of markup types, taking into account the filter by the values of products from the price list, to do this, select the type of markup and click the "Settings" button 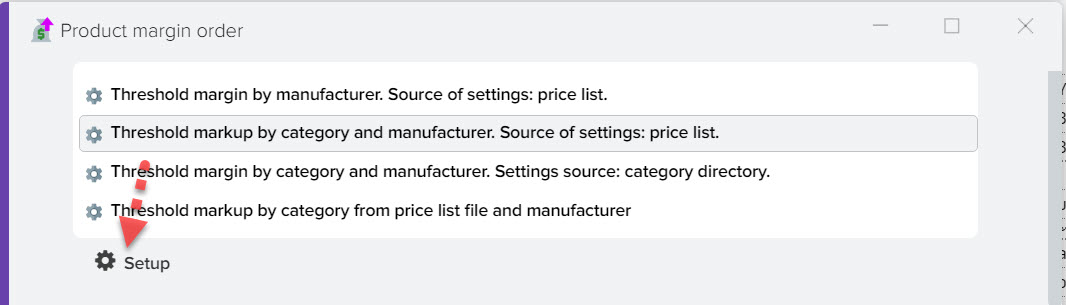
Specify the individual conditions under which this markup type should be triggered. For example, you want to apply a threshold markup taking into account categories only for products from the price list whose price is more than 2000 and the category from the price list does not contain the word "dishes", and for all other products you want to set a different type of markup. 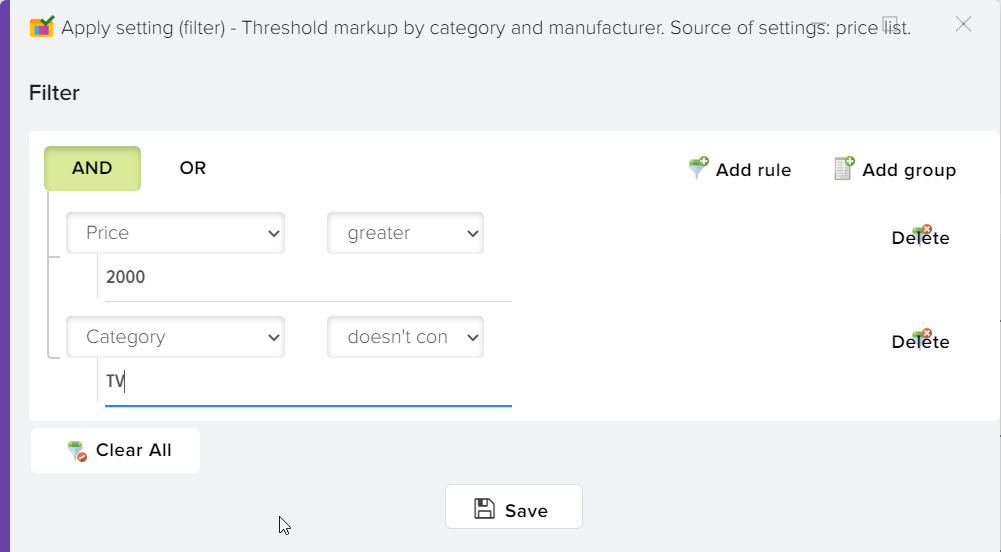
Set up a global markup
The global markup allows you to set a markup for all price lists, with the possibility of applying it only to selected price lists. To configure, open the menu item Directories, Processing price lists, Setting markup 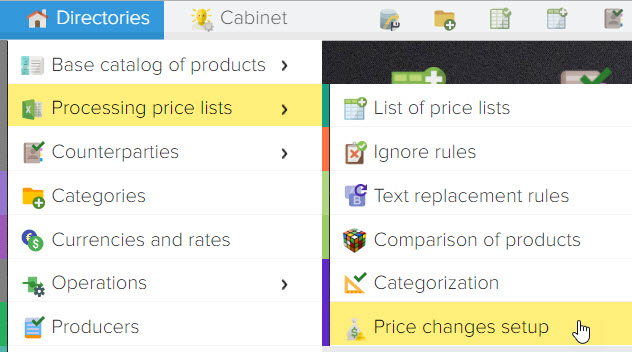
By default, the global markup is disabled for all price lists, to activate it and apply it to the price list, activate this flag in the price settings 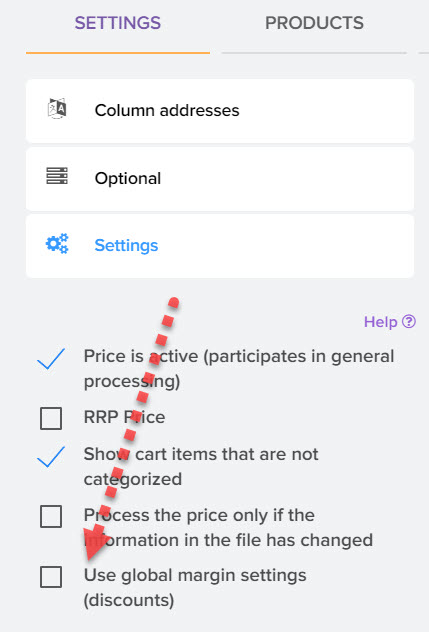
Markup, discount, control RRP, avoid sanctions, increase income
Article source text by Anne Handley
Ann Handley, Content Manager at MarketingProfs blogger, writer, content marketing veteran and digital marketing pioneer. Everyone Writes is a Wall Street Journal bestseller.
- Blog: https://annhandley.com/blog/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/marketingprofs
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ann. handley